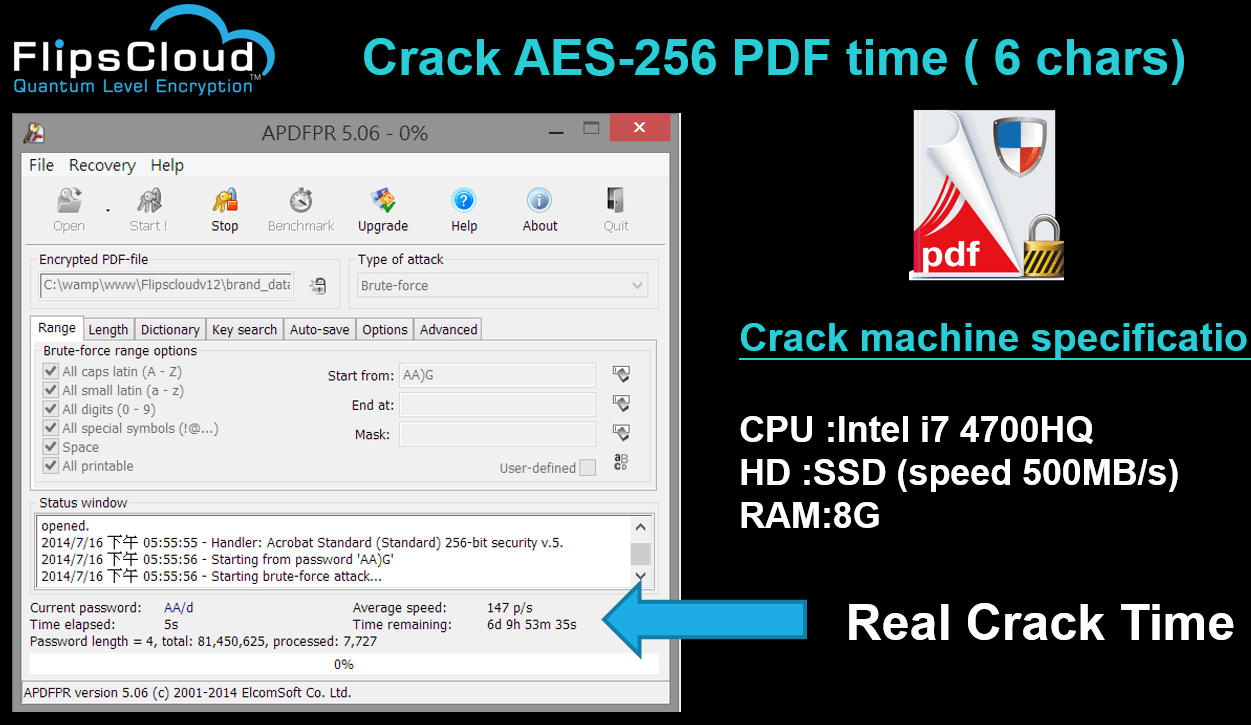
- AES encryption decryption online tool which performs encryption or decryption of an input data based on the given modes (ECB, CBC, CFB or OFB) and key bit sizes (128, 192 or 256 bits) using AES algorithm. The encryption/decryption with a cipher key of 128, 192, or 256 bits is denoted as AES-128, AES-192, AES-256 respectively.
- The result of the AES encryption is a 128-bit number. This is used as the random number output from the generate function. Many security protocols in car access and security require a shorter value due to system response requirements.

AES encryption and decryption online tool for free.It is an aes calculator that performs aes encryption and decryption of image, text and.txt file in ECB and CBC mode with 128, 192,256 bit. The output can be base64 or Hex encoded.
This class provides the functionality of a secret (symmetric) key generator.Key generators are constructed using one of the getInstance class methods of this class.
KeyGenerator objects are reusable, i.e., after a key has been generated, the same KeyGenerator object can be re-used to generate further keys.
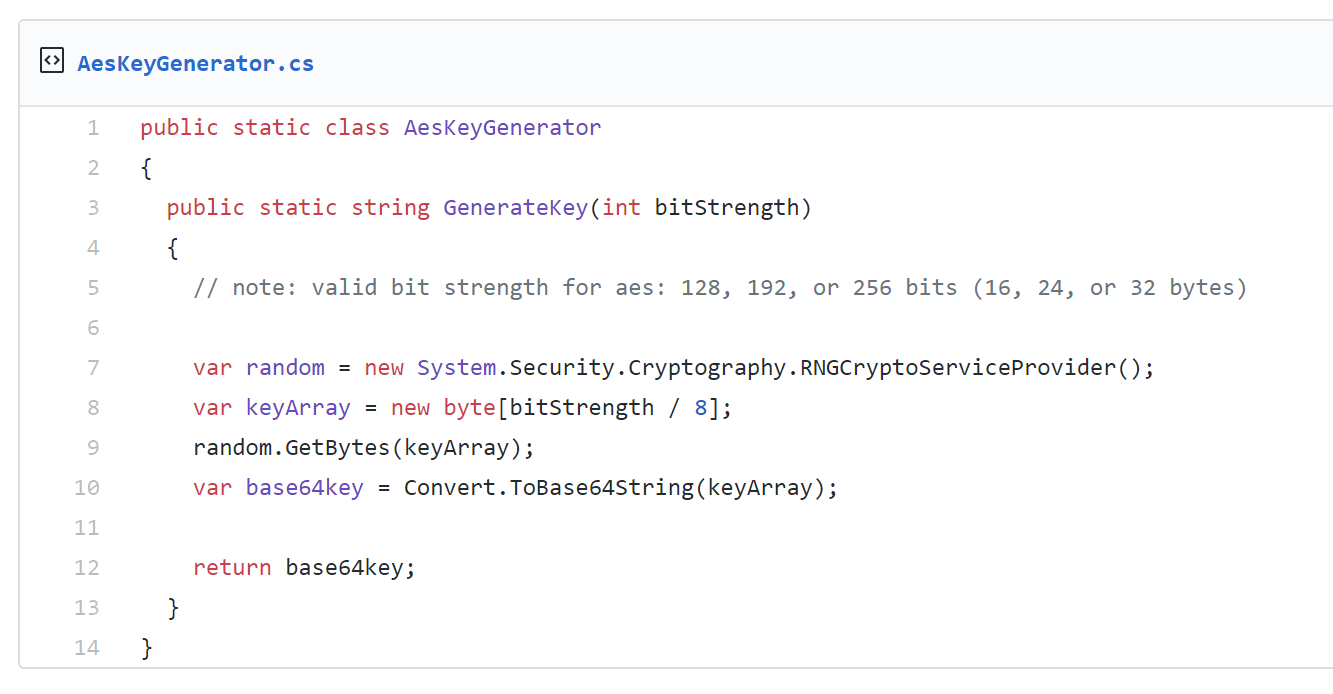
There are two ways to generate a key: in an algorithm-independent manner, and in an algorithm-specific manner. The only difference between the two is the initialization of the object:
- Algorithm-Independent Initialization
All key generators share the concepts of a keysize and a source of randomness. There is an
initmethod in this KeyGenerator class that takes these two universally shared types of arguments. There is also one that takes just akeysizeargument, and uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation), and one that takes just a source of randomness.Since no other parameters are specified when you call the above algorithm-independent
initmethods, it is up to the provider what to do about the algorithm-specific parameters (if any) to be associated with each of the keys. - Algorithm-Specific Initialization
For situations where a set of algorithm-specific parameters already exists, there are two
initmethods that have anAlgorithmParameterSpecargument. One also has aSecureRandomargument, while the other uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation).
In case the client does not explicitly initialize the KeyGenerator (via a call to an init method), each provider must supply (and document) a default initialization. See the Keysize Restriction sections of the JDK Providers document for information on the KeyGenerator defaults used by JDK providers. However, note that defaults may vary across different providers. Additionally, the default value for a provider may change in a future version. Therefore, it is recommended to explicitly initialize the KeyGenerator instead of relying on provider-specific defaults.

Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard KeyGenerator algorithms with the keysizes in parentheses:
Aes 128 Random Key Generator Steam
AES(128)DESede(168)HmacSHA1HmacSHA256